Newsletter-Anmeldung
Verpassen Sie nichts!
Wir versorgen Sie regelmäßig mit den wichtigsten Neuigkeiten, Artikeln, Themen, Projekten und Ideen für EINEWELT ohne Hunger.
Newsletter-Anmeldung
Verpassen Sie nichts!
Wir versorgen Sie regelmäßig mit den wichtigsten Neuigkeiten, Artikeln, Themen, Projekten und Ideen für EINEWELT ohne Hunger.
Bitte beachten Sie unsere Datenschutzerklärung.
Achieving a set of ambitious goals of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the implementation of the Paris Agreement on Climate Change calls for bolder cooperation between public authorities, academic communities, civil society, as well as the private sector. Germany’s development policy engages the private sector to promote and mobilize responsible investment in the agri-food sector in developing and emerging countries.
But what exactly does such a cooperation entail? The following video explains the goals and the roles of diverse actors in development cooperation strategies between the government and the private sector in the agri-food sector.
Funding of development partnerships through German development cooperation requires that long-term business objectives meet sustainable developmental benefits. Strict rules govern such cooperation: It is firstly bound by the international environmental and social guidelines, such as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights; and secondly, by the guidelines of the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ). In doing so, the cooperation seeks to reinforce Germany’s contribution not only to building more sustainable and inclusive economies, but also to upholding socioecological standards.
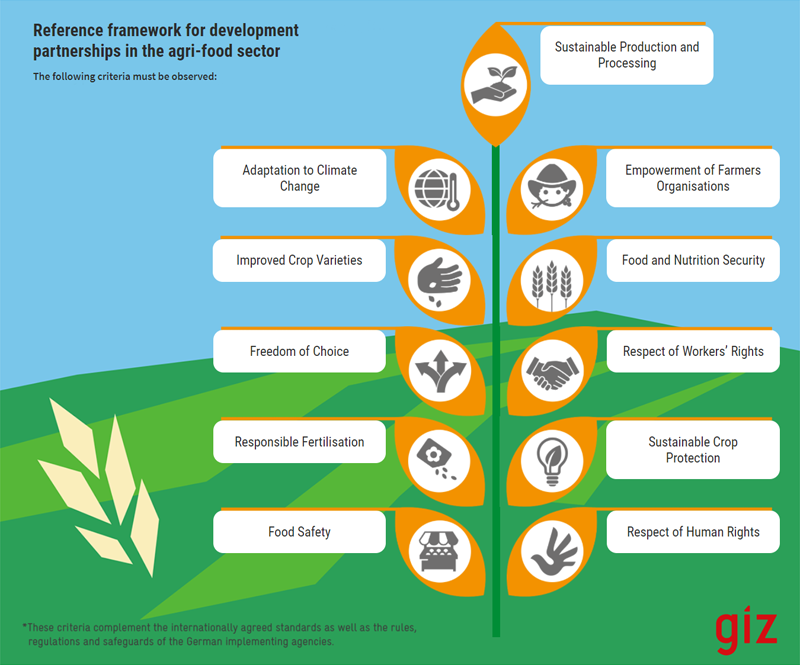
Germany also includes the reference framework for development partnerships in the agri-food sector, which ensures that such partnerships significantly improve the livelihoods of rural communities. The following infographic illustrates the specific requirements for development partnerships in the agri-food sector. These criteria have binding force on all development partnerships in the agri-food sector and equally apply to the implementing organizations of German development policy.
The following criteria must be observed:

Sustainable Production and Processing
Only ecologically, socially, and economically sustainable projects that comply with a human rights-based approach are supported. Sustainable agriculture minimizes water and soil pollution as well as improves soil fertility.

Adaptation to Climate Change
Projects support adaptation to climate change. Innovative measures that reduce greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture are encouraged.

Empowerment of Farmers Organisations
Projects promote agricultural businesses and farmer-based organisations. They strengthen the important role of women in agriculture.

Improved Crop Varieties
Smallholders have access to improved crop varieties. Projects support the sustainable use of genetic resources, and recognize the right to protect traditional knowledge. The right of smallholders to propagate, store, use, exchange, and sell seeds is respected. Projects do not promote the use of genetically modified seeds.

Food and Nutrition Security
Projects contribute to local food security and promote the production and consumption of healthy and nutritious food. Projects with a negative impact on food security are not supported.

Freedom of Choice
The farmers decide freely about their inputs for production. Project partners provide fair and transparent advice and do not give recommendations that are limited to the use of their own products.

Respect of Workers’ Rights
The core labour standards of the International Labour Organization (ILO) apply to all projects, including freedom of association, the right to collective bargaining as well as the elimination of forced labour, child labour and discrimination in the workplace.

Responsible Fertilisation
All projects promote the use of fertilisers for a balanced supply of nutrients and long-term preservation of soil fertility. They take into account local climate, soil conditions, and specific crop requirements. Organic fertilisers and nutrient recycling methods are preferred.

Sustainable Crop Protection
Projects promote sustainable crop protection strategies based on the principles of Integrated Pest Management (IPM). Project partners commit to complying with the FAO/WHO International Code of Conduct on Pesticide Management. For the procurement of pesticides, the rules and regulations of the German implementing agencies apply.

Food Safety
Agricultural products and manufacturing processes comply with internationally recognized food safety standards.

Respect of Human Rights
Participating companies respect human rights in accordance with the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights. To this end, the establishment of a human rights risk management system in accordance with OECD Due Diligence Guidance is recommended.
Cooperating with the private sector works! Germany’s development policy aspires to accommodate the interests of enterprises, while at the same time enhancing societal development that are built around the three pillars of sustainability goals. This partnership mechanism would benefit all stakeholders involved in the agri-food sector and thus contributes to its efficiency.
A successful public-private partnership allows for necessary synergies and increases sustainability. The following video testimonials highlight the added value through such partnerships from various perspectives and projects.
For more information on the cooperation with fairafric in Ghana, click here..
For more information on the cooperation with Amru Rice in Cambodia, click here.
For more information on the Sustainable Aromatic Rice Initiative in cooperation with Mars Food and HERBA in Thailand, click here.
For more information on the cooperation with Continental in Indonesia, click here.
For more information on the cooperation with Harmless Harvest and Danone Ecosystem Fund in Thailand, click here.

Prerequisites, impact pathways, opportunities and guidelines (German)

Overview of further funding, financing and cooperation opportunities (German)

Technical Guidelines
In case you have any questions or suggestions, please contact the Sector Project Agriculture at agriculture@giz.de